FlexDyn
Steady-state (power flow) and dynamic stability analysis
T. Demiray, “FlexDyn: An RMS-based dynamic stability analysis tool for very-large interconnected electric transmission systems”, 2017.
- Performs static & time-series power flow analysis & dynamic stability analysis for electric transmission and distribution systems.
- RMS simulations are performed in a rotating dq-frame, allowing computationally-efficient simulations of large power systems.
- Built-in standard dynamic component and controller models such as governor, AVR, PSS, SVC/STATCOM, etc.
- Flexible integration of new user-defined components and controllers, such as those for converters and converter-interfaced systems.
- Symbolic model definition capability, automatically translated to C++.
- Input data format is JSON.
- It can be operated in different operating systems such as Windows, Unix, Linux, and Mac OS X.

Publications:
Turhan Demiray and Göran Andersson, Optimization of numerical integration methods for the simulation of dynamic phasor models in power systems, International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, vol. 31, no. 9, 2009, pp. 512-521. (also presented at Power Systems Computation Conference, PSCC 2008) [external page doi]
Turhan Demiray, Simulation of Power System Dynamics using Dynamic Phasor Models, Doctoral Thesis, Zürich, ETH Zürich, 2008. [external page doi]
Turhan Demiray, G. Andersson and L. Busarello, Evaluation Study for the Simulation of Power System Transients using Dynamic Phasor Models, IEEE/PES Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition: Latin America, August 13-15, 2008. [external page doi]
Turhan Demiray, Federico Milano and Göran Andersson, Dynamic phasor modeling of the doubly-fed induction generator under unbalanced conditions, IEEE Powertech, July 1-5, 2007. [external page doi]
Turhan Demiray and G. Andersson, Comparison of the efficiency of dynamic phasor models derived from ABC and DQO reference frame in power system dynamic simulations, IET International Conference on Advances in Power System Control, Operation and Management (APSCOM 2006), October 30 - November 2, 2006. [external page doi]
ENTSO-E model:
- 24’000 Nodes
- 30’000 Branch elements (overhead, cable, transformer)
- 7’000 Loads and 5’000 static generators (impedance models)
- 1’000 Synchronous generators (dynamic 6th order machine model, Governor, AVR and PSS)
The accuracy of the model import and the plausibility of the simulation results have been validated within the recently completed project SCCER-FURIES (joint work with Swissgrid) [1]. The model snapshot captures a high-load case with a total load of about 458 GW over the ENTSO-E area.
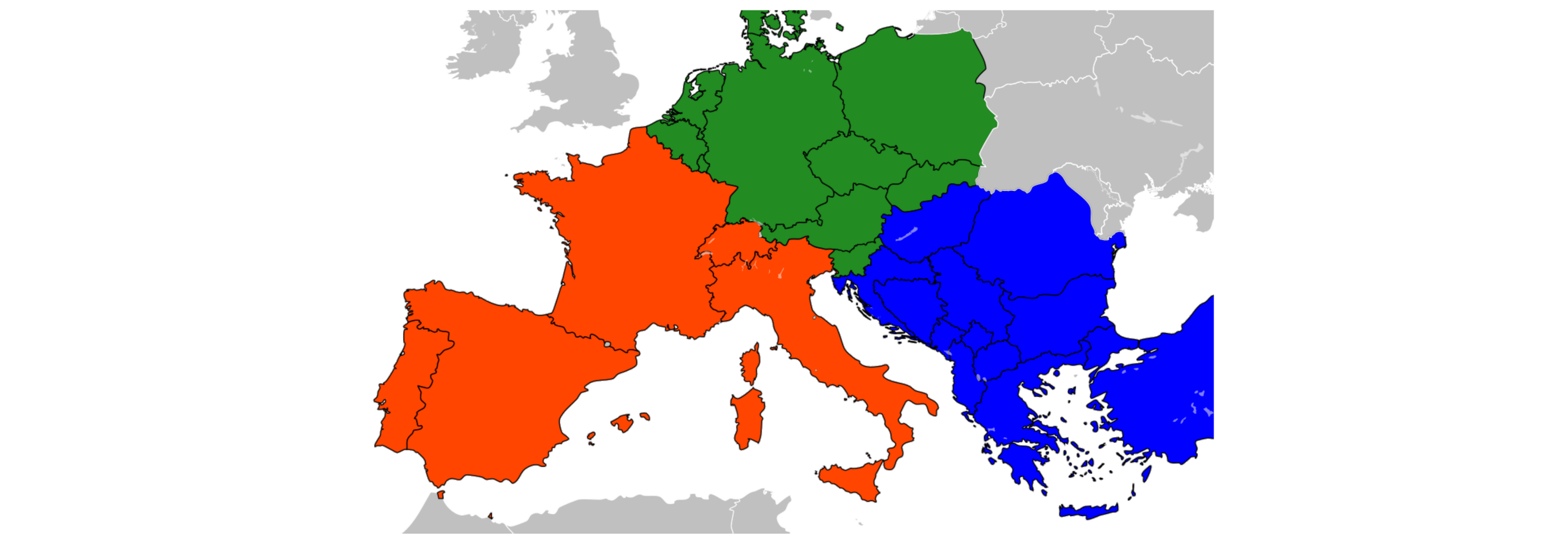
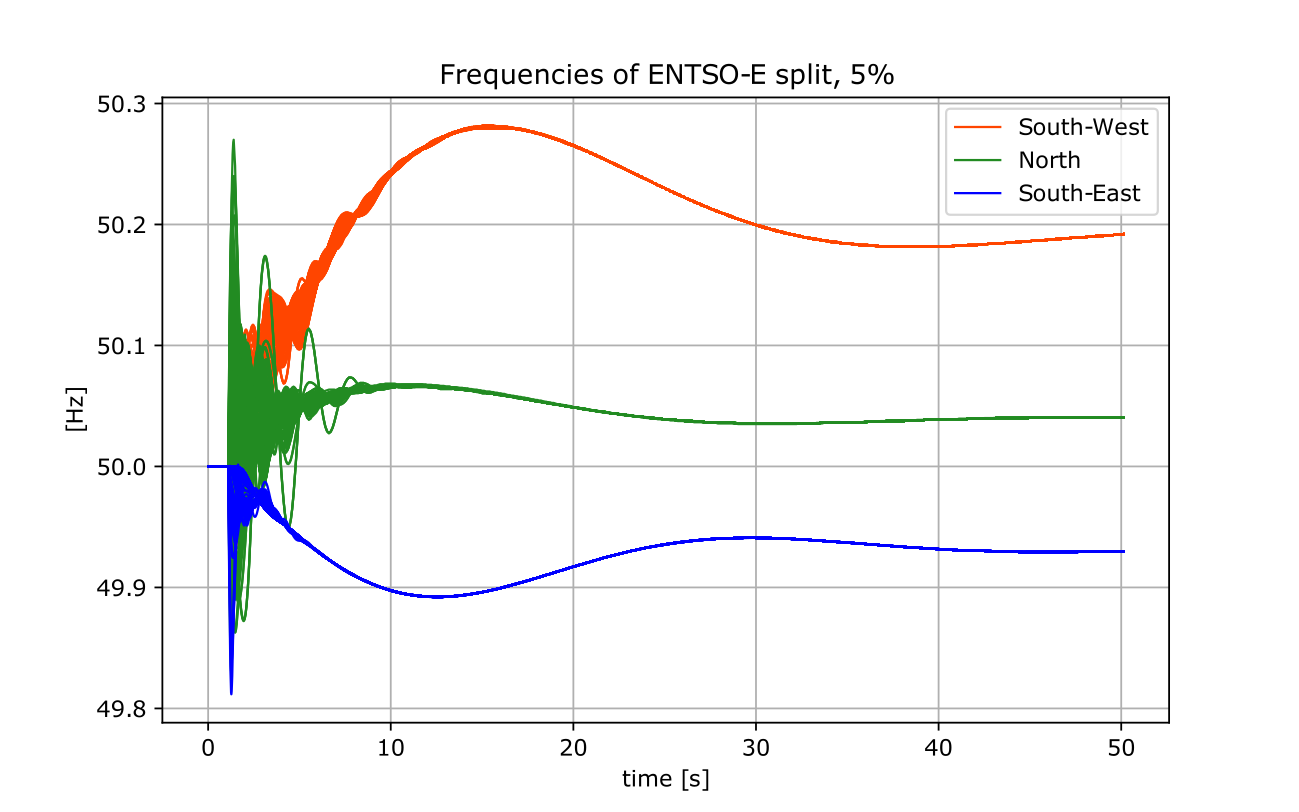
References:
[1] Alexander Fuchs. Dynamic Transmission System Emulator for Stability Assessment, SCCER-FURIES Annual Conference, 2020. [external page Presentation & Video]
[2] ENTSO-E. external page Final Report System Disturbance on 4 November 2006, 2007.